Constitutional Monarchy Examples and Facts
For most English speakers, the United Kingdom and Queen Elizabeth probably come to mind when thinking about a monarchy.
But the UK isn’t the only country with a constitutional monarchy!
If you want to learn more about monarchies, consider how to define monarchy versus other government structures. Then, you can use that definition to learn more about examples of constitutional monarchies.
Related: US Constitution & Government
Constitutional Monarchy Definition
The constitutional monarchy definition states this type of government uses the nation’s constitution to limit the powers of the monarchy.
A monarchy has a ruler, and most fill that role with a king or queen.
While a monarch may have some power, the constitution dictates what the monarch can and can’t do.
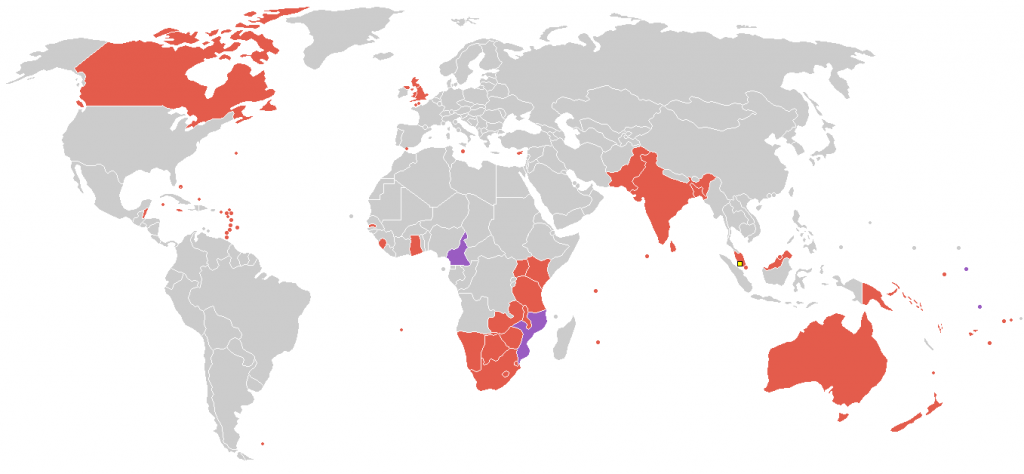
Constitutional Monarchy Examples and Facts
There are many constitutional monarchies around the world. Here are some examples and facts about each one.
The United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is probably the most famous constitutional monarchy. Currently, the monarch is Queen Elizabeth II, and she has been the monarch since 1952.
Along with the United Kingdom, the constitutional monarchy includes the Commonwealth Realm. Because of this, many other countries share the same monarchy.
Countries include:
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Barbados
- Belize
- Grenada
- Jamaica
- Canada
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Solomon Islands
- Papua New Guinea
- St. Vincent and the Grenadines
- St. Lucia
- St. Kitts and Nevis
- The Bahamas
- Tuvalu
Some of these countries are in the Americas, while others are in Oceania. Each country in the Commonwealth has a prime minister or representative.
However, the British monarch is the head of state for these other countries.
Others in Europe
While the United Kingdom is perhaps the most famous constitutional monarchy, other European nations share the same form of government.
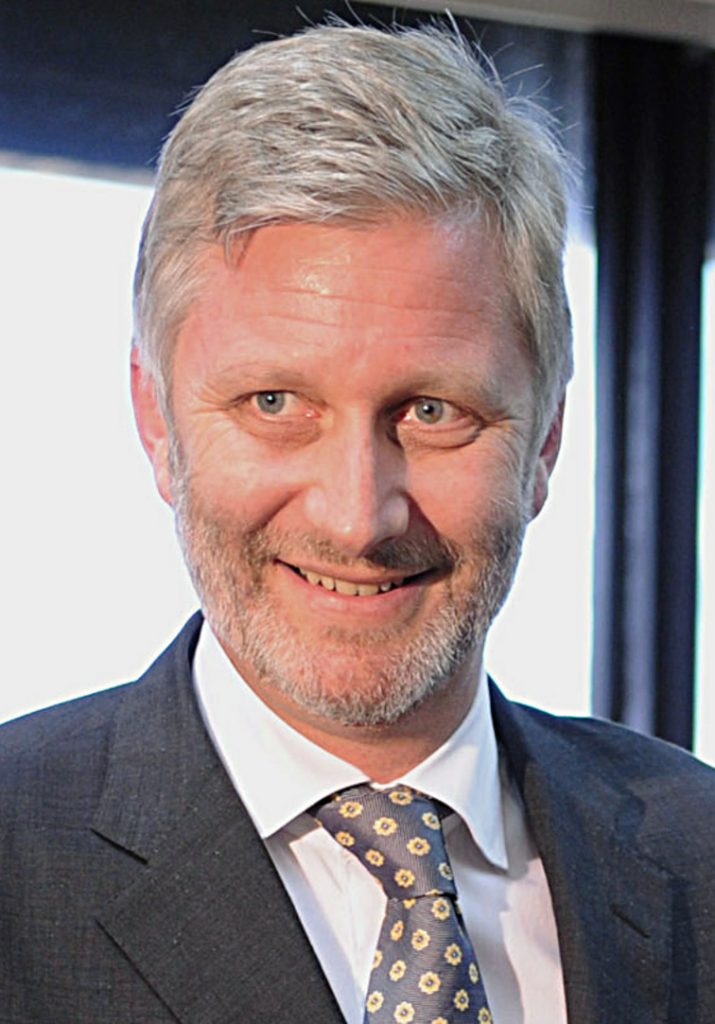
Belgium has a constitutional monarchy, and the current head of state is King Philippe. He became king in 2013.

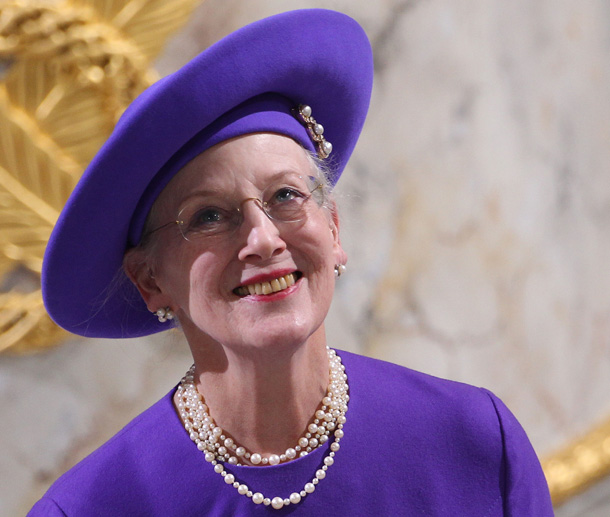
In Denmark, the government is a constitutional monarchy and a democracy. The current monarch is Queen Margrethe II, but she does not have any power over the country.
The monarch of Liechtenstein works with the democratically elected parliament. Unlike some monarchies, the Prince of Liechtenstein is very active in politics and helps rule the country.
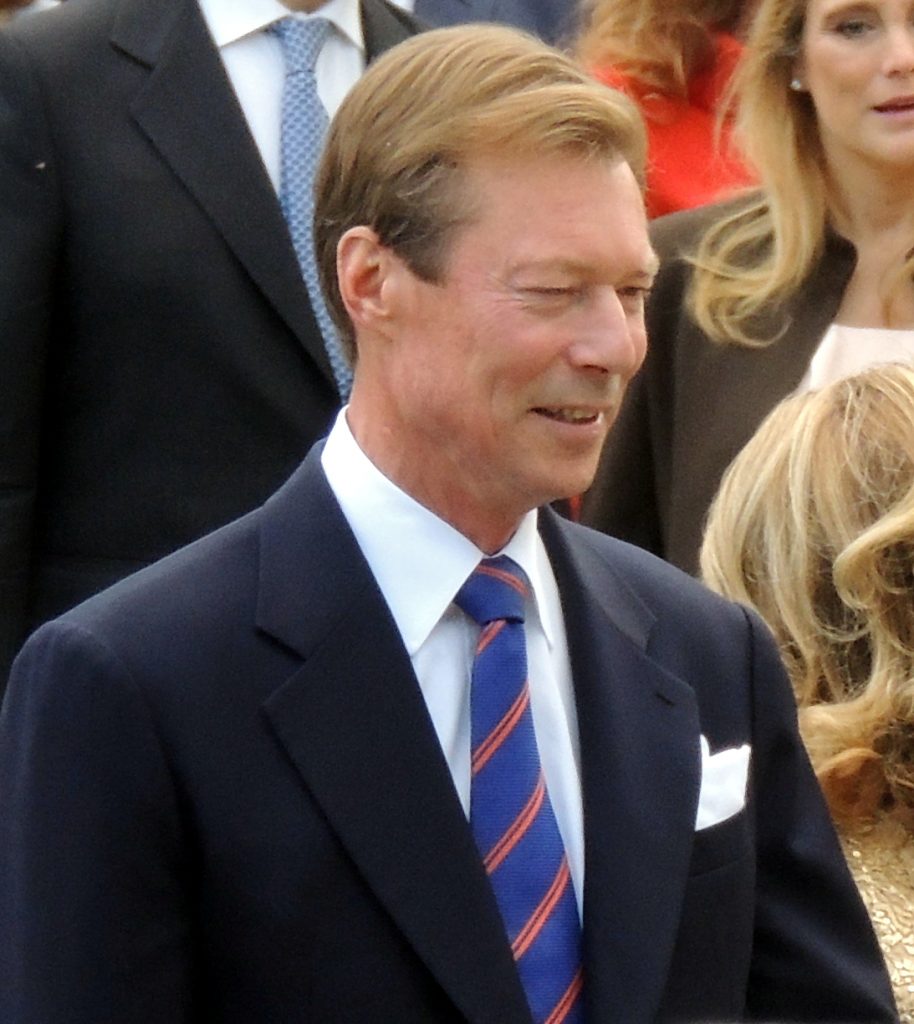
Luxembourg has a constitutional monarchy, and the head of state is the Grand Duke Henri. The country also has a democratic form of government, and the Grand Duke enacts laws that the government passes.

In Monaco, the current monarch is Prince Rainier III. He has power, and the role moves through a hereditary line of succession.
The monarch works with the parliament to govern the country.
The Netherlands has a king or queen that works with the ministers. While the monarch has some power, parliament is in charge of making governmental decisions.
The monarch of Norway is primarily a ceremonial role, and he or she works with the rest of the government.

People in Norway elect other government officials, and those officials have most of the power.
Spain has had many monarchs over the past few centuries. Like other countries, the monarch doesn’t have much power.
Instead, an elected body of officials, including a prime minister, has more control over the country.
In Sweden, the queen or king does not have any power and is more of a public figure. The role is passed down through families to the first-born, regardless of gender.
Asia and the Middle East
Asia and the Middle East also have many constitutional monarchies.
Here are a few states with this government structure and some relevant constitutional monarchy facts:
In Bahrain, the king appoints the prime minister and the Council of Ministers. However, adults in the country do elect the Chamber of Deputies.

Bhutan’s monarchy follows the traditional family lineage. The monarch has had more power in the past, but the country has started to become more democratic thanks to changes to the constitution.
After a switch between an absolute monarchy and constitutional monarchy, Cambodia has settled on the latter.
However, people in the country should not insult the king because that is a sign that someone may try to overthrow the monarchy.

In Jordan, the monarchy has power over the various branches of government. The king appoints the prime minister, but the parliament has to approve the appointment.
Kuwait has a more open constitutional monarchy than other monarchies in the region. The ruling family controls the cabinet, which works with the parliament to govern the country.
The Malaysia monarchy has federal and state parliamentary democracies. While the king is in charge of the armed forces, he has to work with the parliament to successfully rule the country.
Thailand’s monarchy has faced criticism and controversy, but it still follows the constitution. Succession follows the family line, and the monarch helps the government and the people.
Africa
While Africa doesn’t have as many monarchies as other continents, there are some. Below are some African countries with a constitutional monarchy.
Lesotho’s current monarch is King Letsie III. He has served as the king since 1997, and his wife serves as the monarch when he is out of the country.

In Morocco, the monarch has struggled to balance his power with that of the parliament. However, the country’s constitution lays out guidelines for how to organize the parliament and monarchy.
Oceania
Oceania comprises Australia, New Zealand and small islands in the region. Here are a couple of constitutional monarchies in the area and some constitutional monarchy facts.
Samoa had two monarchs under a traditional constitutional monarchy. However, after that, the country decided to make the position one that the Legislative Assembly would elect.
Now, the monarch can serve no more than two five-year terms.
In Tonga, the monarch works with an elected parliament to rule the country. However, the change came about fairly recently, and Tongan monarch had more power for many years.
Constitutional Monarchy Information
A constitutional monarchy is a type of government that involves a king or queen.
Related on the Blog: Famous Child Kings
However, the monarch may not have much or any power. Instead, elected officials, such as the British parliament rule the country.
However, there are different systems of constitutional monarchies around the world. Sometimes, the head of state has more power, but other times, the monarch may not have power.
Despite the differences, a constitutional monarchy is a popular form of government. So it’s important to understand how it works in various countries.