Muscle Facts
When you think about muscles, you probably think of strong arms or abdominals. But did you know that your heart is a muscle too?
Your muscles help you pump blood throughout your body, move, and lift heavy objects.
You control some of your muscles, but others (like your heart) work on their own.
In fact, you have over 600 muscles in your body!
There are three different types of muscles: smooth, cardiac, and skeletal.
All of these muscles are made up of thousands of small fibers, and they’re all made of the very same material: a sort of elastic tissue that feels similar to a rubber band.
Now let’s look at what makes each type of muscle different.
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscles are sometimes called involuntary muscles because you can’t control them. You don’t even have to think about it—your brain and body instruct these muscles on what to do all by themselves.
Smooth muscle usually come in layers, with one layer of muscle located behind the other. These muscles help with digestion by contracting (tightening) and relaxing to help food pass through your body.
They’re also located in the bladder, where they relax to help you hold your urine and then contract to push the urine out (use the restroom).
Similarly, they’re found in the uterus and help women have babies.
In your eyes, smooth muscles help you focus on the objects and images around you.
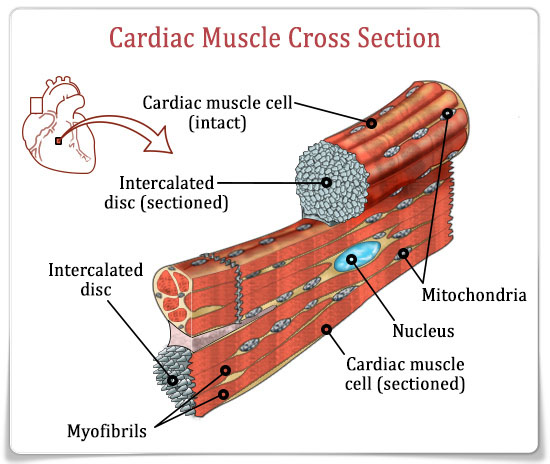
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle is also known as the myocardium, and it’s the muscle that makes up your heart. These thick muscles contract to pump out blood to the rest of the body.
After blood has circulated around the body, these muscles then relax, to allow blood to flow back in to the heart.
Like smooth muscle, cardiac muscle works without any thought from you. It works on autopilot!
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle, also called striated muscle, is the type you probably think about when you hear the word “muscle.”
These are the muscles people work out in the gym, the ones that allow you to lift heavy weights, swim, and run.
These are muscles that you can control. They’re part of the musculoskeletal system, which refers to your muscles and bones.
These muscles are held to your bones with tendons, cords made of tough tissue that connect bone and muscle.
Your skeletal muscles give you power and strength, keep you standing straight and tall, and help you hold your head high.
Examples of skeletal muscles
Biceps
When you flex your arm, the muscle that pops up is your bicep. Many people develop these muscles by lifting weights.
Quadriceps
Also called quads, these muscles are located in your thighs. These muscles are often strong in soccer players, cyclists, runners, and other athletes.
Rectus abdominus
These muscles are called abdominals, or “abs” for short. They’re located under your ribcage.
Pectoralis
The pectoralis muscles are also called pectorals, or “pecs” for short. These muscles are on your upper chest and are often very large on bodybuilders or athletes.
Fun Facts About Muscles
Muscles make up about 40% of your total body weight. This is why athletes with very little fat can still weigh a lot.
You are born with all the muscle fibers you’ll ever have. These fibers grow thicker, but you don’t grow new fibers.
It’s true that it takes more muscles to frown than to smile. Frowning uses 43 muscles, while it only takes 17 to smile!